Chapter 4. Types of conversion operations
The concept of the type of conversion operation at Forex is closely intertwined with the terminology of financial instruments. In financial markets, which in addition to Forex also include the gold market, credit market and securities market, financial instruments are understood as ways of carrying out financial transactions. Below we will consider only financial instruments related to the international currency market Forex. Other financial markets and their financial instruments are beyond the scope of the information portal Forex Arena and will not be considered further. Types of conversion operations (financial instruments related to Forex) are shown in the figure.
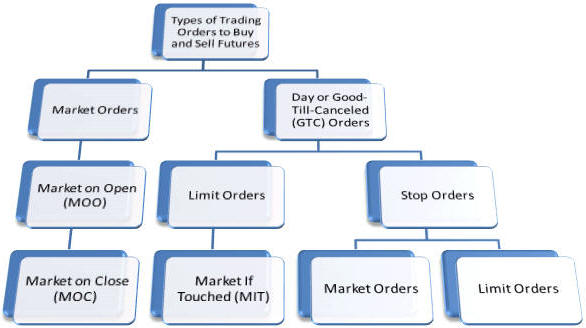
A conversion transaction is a transaction of Forex participants to exchange a specified amount of currency of one country for the currency of another country on a certain date at an established quotation. Conversion operations at Forex are distinguished by the value date, i.e. the date of delivery of currency relative to the date of conclusion of a currency purchase/sale transaction. According to this feature conversion operations can be divided into two categories, as shown in the figure:
spot or current conversion transactions;
forward conversion operations.
The largest volume of operations on Forex is occupied by spot operations. It is the work on Forex on these operations that is considered on the information portal Forex Arena. In international practice it is accepted that the value date of spot transactions is the 2nd working day after the conclusion of the transaction. Such conditions are quite convenient for the counterparties (participants) of the transaction, as during the current and the next working day it is possible to process all the necessary documentation and execute payment documents. The market where currency is exchanged at current (spot) quotations is called spot market.
It should be noted that this principle of mutual settlements on spot transactions is valid only for large participants of the international currency market. For private investors (clients of retail brokerage houses) working on Forex via the Internet, the transaction is made instantly at the click of a mouse button. In such transactions the value date as such loses its meaning – the client’s account always reflects the current state of his work on Forex.
Forward conversion transactions include forwards, futures, options and swaps. They are also called derivatives. Such financial instruments have been specially developed for real business, as they allow to reduce possible risks from changes in quotations on the international currency market in the future. For a private investor wishing to make money on Forex via the Internet, such financial instruments are of little importance. Nevertheless, they will be considered to understand the general picture of types of conversion operations.
Forwards (forwards) or as they are also called – forward contracts, are concluded between the participants of the transaction on the condition of exchanging a certain amount of currency at predetermined quotes on a predetermined day (value date). The transaction will be made regardless of what the current (spot) prices will be on the Forex currency market on the value date. The amount of the transaction, quotes and value date can be any – it all depends on the agreement reached by the counterparties.
Forward contracts on Forex can be useful, for example, when a Russian company plans to purchase equipment for US dollars abroad. Let’s imagine that such a company does not have enough cash for the transaction at the moment, but expects to receive cash in rubles on its current account within a month. It also expects the exchange rates to change to its disadvantage, i.e. the dollar is expected to appreciate. In such a case, it makes sense to enter into a forward contract with a bank to purchase the required amount of US dollars with a value date of one month at quotations favorable to the company. Naturally, the bank may not agree to such conditions if it also expects the US dollar to rise in value, and finding a counterparty for such a deal may become a difficult task.
Forward contracts on the one hand minimize risks, but on the other hand can become a source of lost profit. For example, if in the previous example, in a month from now the US dollar will become cheaper instead of more expensive, the company will have lost profit. After all, the company could have paid less rubles for the equipment.
Futures (futures), unlike forward contracts, have standard maturity dates (value) and fixed amounts of currency. This feature allows them to be traded as ordinary securities. There is a separate market for futures trading at Forex – the futures market. The average duration of futures circulation on this market is approximately 3 months.
Options are similar to futures, but they weaken the obligations of one of the transaction participants. Thus, if when buying a futures you are obliged to make a transaction according to the agreed terms of the deal, in the case of an option, you can refuse to carry out the transaction at your discretion. Options on Forex are also traded on a separate market – options market.
Swaps – a type of conversion operation, in which the parties conclude a deal to buy/sell a certain amount of currency with the obligation to make a reverse transaction after a certain period of time. For example, a company buys USD 1,000 for rubles at the current (spot) quotation from a bank with the obligation to sell USD 1,000 for rubles to the bank in a month at the current (spot) quotations that will be on Forex in a month. Swaps are non-standardized contracts, so they are not traded on a separate market.
Of all the described conversion operations (financial instruments) for a private investor wishing to earn money on Forex via the Internet, the most important are spot operations on the spot market. It is the spot Forex market that is discussed in detail in the following chapters of the Forex Arena information portal.
This can be interesting:
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Forex
- Chapter 2: Forex Participants
- Chapter 3: Forex Currency Designation
- Chapter 4. Types of conversion operations
- Chapter 5. Forex Currency Quotes
- Chapter 6. Buy/sell rates and spreads
- Chapter 7. Cross-courses
- Chapter 8: Forex Mode of Operation
- Chapter 9. Forex and Exchange
- Chapter 10. Margin trading
- Chapter 11. Margin call
- Chapter 12. Bank interest
- Chapter 13. Income of Forex Participants
- Chapter 14. Calculation of profits and losses
- Chapter 15. Comparison of Forex and Casinos
- Chapter 16. Comparison of Forex and Stock Market
- Chapter 17. Stock Exchanges and Stock Indices
- Chapter 18. Commodity currencies at Forex (Commodity currencies)
- Chapter 19. George Soros – the story of one trader
- Stocks or bonds? What to choose for a novice investor? Video

